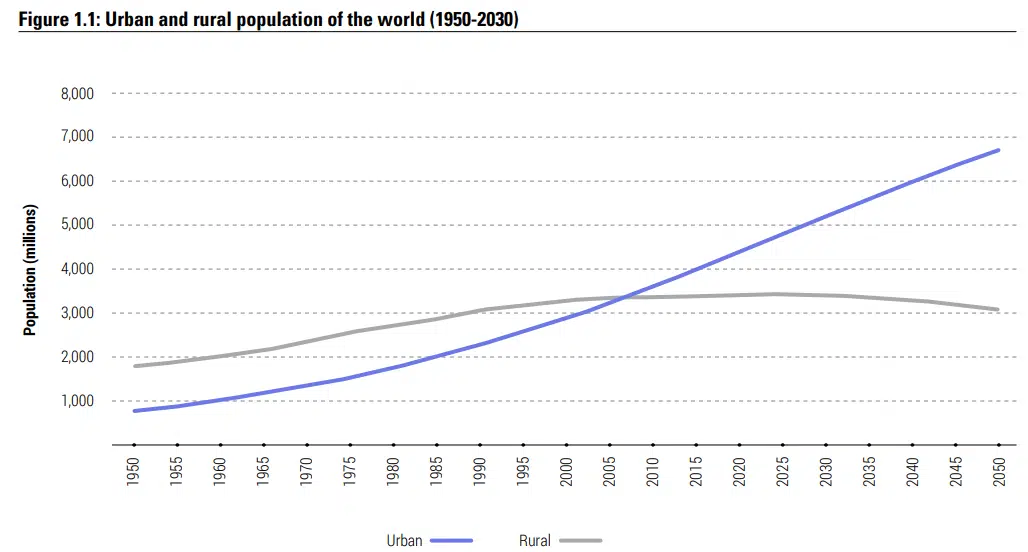
Author | Jaime RamosThe number of people aged 60 years or older will rise from 900 million to 2 billion between 2015 and 2050, according to the World Health Organization. This will mean an increase of 10%. Are urban environments prepared for this pace of population aging?In demographic terms, higher life expectancy is one of the main reasons for this phenomenon. By 2050, an increase of 5 years is expected, bringing the average length of life globally to 77.1 years. One of the direct results of the existence of an older population is the higher proliferation of diseases associated with their age group.
Do urban environments have an effect on cognitive responses?
Alzheimer’s is one of the most common diseases among older people. The Alzheimer’s Association in the United States indicates that 10% of people age 65 and older has this disease. Associated with the loss of memory, Alzheimer’s leads to increasingly severe degenerative symptoms as a result of a process in which connections between networks of neurons break down.Given its characteristics, the disease requires a high level of care. Because nobody should face this type of cognitive impairment alone. Fortunately, experts, such as the urban planner Samantha Biglieri, have identified areas of invention that could facilitate the lives of people with Alzheimer’s.
What can cities do to help people with Alzheimer’s?
Urban planning models
The development of smart urban layouts can contribute, not only to making life easier for people living with the disease, but also to the prevention of the early onset of the disease. Scientists are working on demonstrating the relationship between some aspects of existing urban problems, such as air quality and the development of cognitive diseases.
Open-air urban spaces
Urban planning can have extremely beneficial effects on the quality of life of people affected by dementia. The key lies in creating adapted and open-air environments that enable them to deal with the disease. To do so, an in-depth study needs to be conducted to establish the different stages of neurodegenerative diseases and the urban possibilities.
Exercise and social interaction
According to Biglieri, exercise and social interaction are essential. Her work has led her to identify efficient methods to combat the disorientation process experienced by people living with Alzheimer’s. The idea is to improve elements related to urban design in a way that facilitates mobility throughout city centers.
Innovate with sensory routes
In the case of Alzheimer’s, Biglieri indicates that it is important to design spaces with specific elements that serve as solid sensory references using the countless possibilities of street features: paving, gardens, fountains, signs, etc.
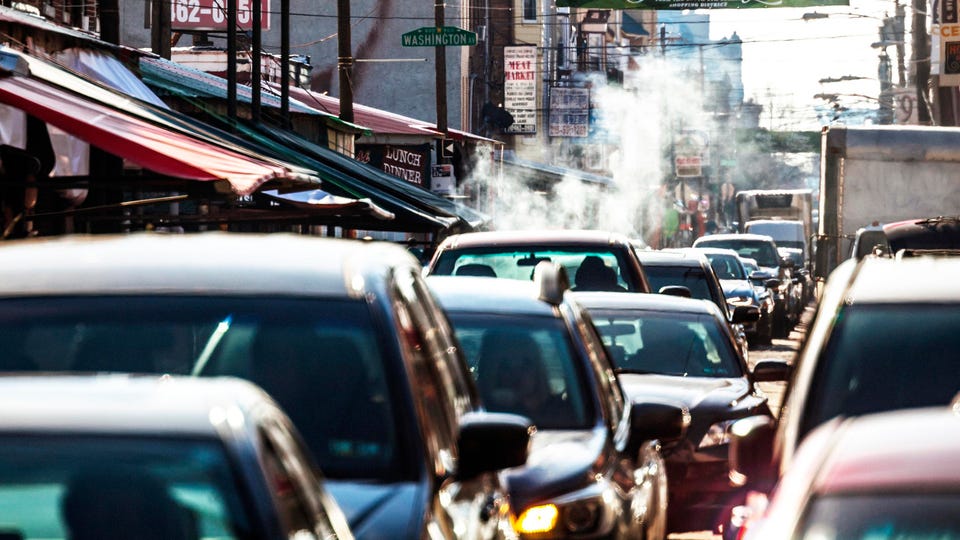
Within this trend, the existence of extensive pedestrian areas is exceptionally relevant. A city that promotes walking is immensely valuable to people living with dementia, enabling them, within their possibilities, to adapt their habits to this form of mobility.Likewise and as a factor to be taken into account in the long term, diseases such as Alzheimer’s require sustainable and emission-free environments. There are studies, such as this one conducted in Barcelona, which directly relate air pollution and neurodegenerative diseases. There is now evidence to suggest that the brain’s white matter degenerates with the air pollution caused by combustion engines.Scientists agree that reducing air pollution in urban environments is essential. This is why, when redesigning the cities of the future, issues such as the space reserved for vehicles and the change to emission free engines, such as 100% electric vehicles, has become particularly relevant. An extremely promising benefit with the potential to prevent and ease the impacts of neurodegenerative diseases.Images | iStock/NanoStockk, iStock/morpheuse, iStock/Bulat Silvia