Author | M. Martínez Euklidiadas
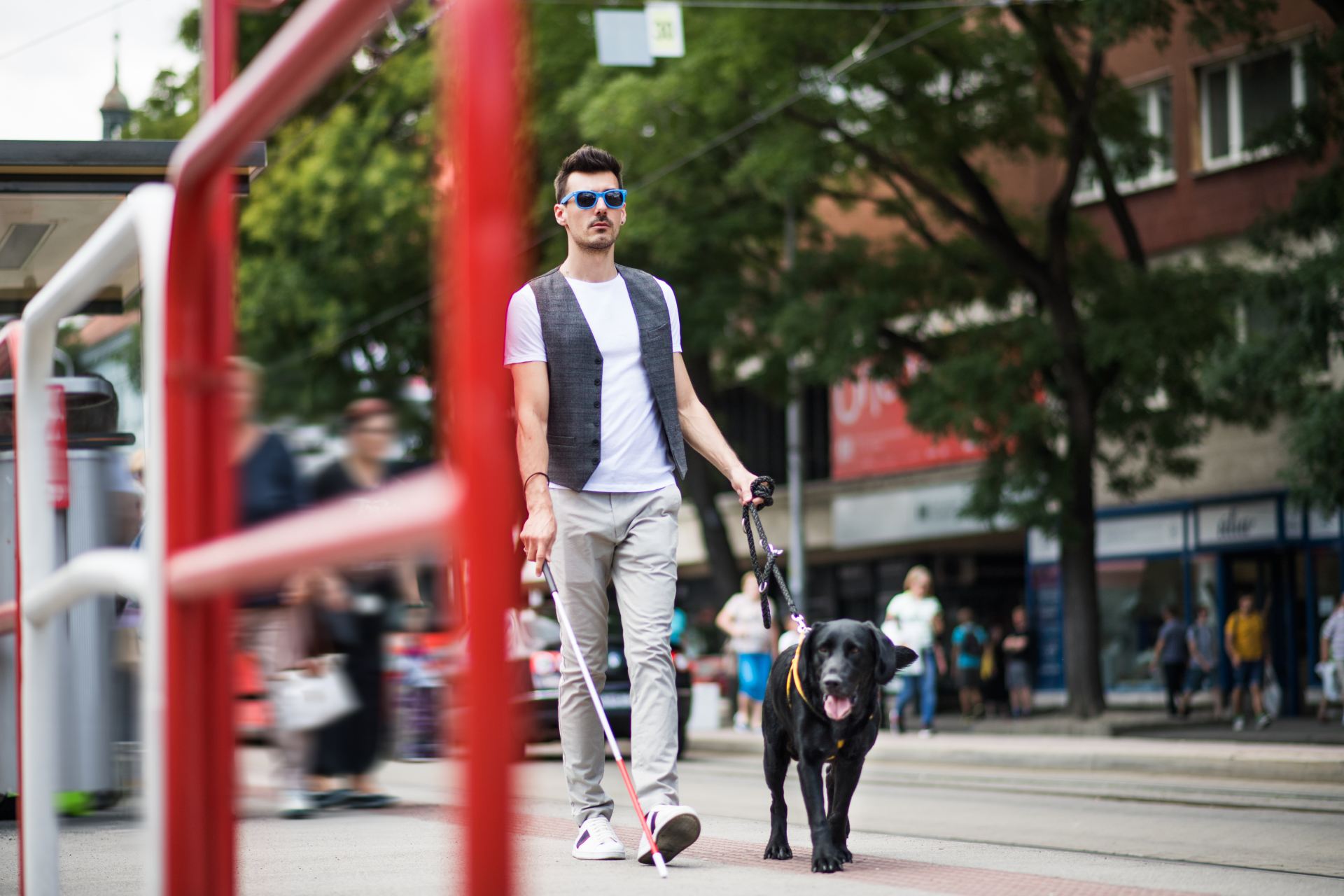
According to the WHO, around 1.3 billion people in the world are affected by some form of visual impairment, of which at least 36 million are completely blind and 217 million have a moderate to severe visual impairment. Given that an increasing number of people are living in cities, it seems logical to facilitate the lives of people living with visual impairments through accessibility.
What is smart technology and how can it help visually impaired people?
The Global Compact on Inclusive & Accessible Cities declaration, presented during the International Day of Persons with Disabilities (2019) and within the scope of the Cities for Everyone project —aligned with the New Urban Agenda or, the Sustainable Development Goals— is__ a global commitment to make cities more accessible.__
Technology plays an essential role in this commitment. In fact, it is imperative for smart cities to generate adapted technology to prevent it from becoming a barrier, since smart technology is technology that can be used by everyone.
As an example of bad use of technology, in 2016, the American Federation for the Blind sued New York City because the LinkNYC system, which offers Wi-Fi, charging points and a place in which to carry out procedures, was not only not adapted for visually impaired users, but it was in fact an architectural barrier.
Assistance for blind people in cities: tactile maps, orientation apps and other smart technologies
Historically, touch has played an important role in the integration of blind people. It is easy to find tactile tourist maps, sentences in braille format or tactile paving that guide people. However, technology is opening more possibilities and audio technology is set to become the next major revolution, combined with artificial intelligence.
The Google Lockout application is one of the tools being developed, which enable visual data detected by a smartphone camera to be transformed into audio format. This allows objects to be located, signs to be read and even to understand labels, although it will still take a few years for it to become a useful tool. Luckily, other urban tools are being deployed:
Bluetooth beacons for smart cities
The Wayfindr project is an open standard via which, the visually impaired can be guided through complex environments using a Bluetooth beacon system and 5G networks. Successfully tested in the London Underground system, this standard could become one of the main forms of navigation for visually-impaired and blind people, but also for any other user.
BART Maps (Tactile Mapping Project)
For years, tactile graphics have been the Holy Grail of urban maps for the visually impaired. However, they still need to improve much more, by integrating layers of audio or making them more accessible. That is the aim of the San Francisco Bay public transport Tactile Mapping Project, which has spent years designing a tactile and audio standard to represent the 44 stations in the region.
Lazarillo: navigate any city using an app
Lazarillo is an app for getting around any city. Aimed at navigation through audio, the app informs users of the street they are walking along, other nearby streets, the stores, services or transport available nearby or how to walk from one place in the city to another.
By definition, a smart city must take into account the different needs of its population. And this includes the elderly, people with difficulties in getting about, people with different levels of visual impairment, deafness and other disabilities affecting their autonomy. They also form an integral part of cities.
Images | iStock/Halfpoint