Author | Lucía Burbano
In recent decades, many global cities with a strong industrial past have had to reinvent themselves in order to respond to the decline experienced by many sectors. The solution in many cases has been to find new niches that reinterpret a legacy not completely disassociated from smoke and soot, choosing attractive options related to culture, services, architecture or history.
From industrial cities to contemporary centers
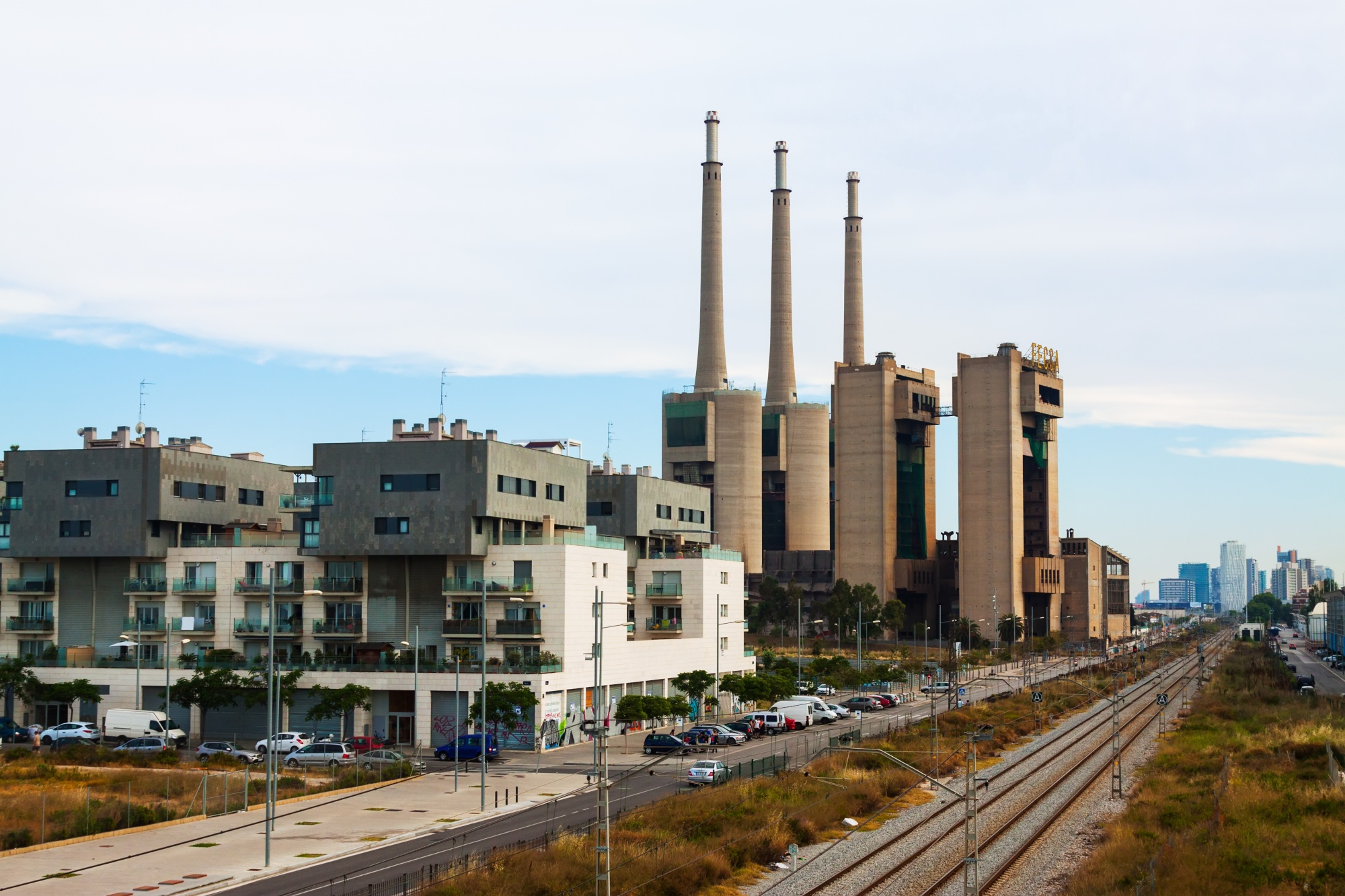
After the factories that had once dominated the industrial urban landscape had closed their doors, cities that wanted to survive their past had to resort to different strategies** to reinvent themselves** in order to attract tourists, companies, knowledge, investors or entrepreneurs.
These strategies raise essential issues that need to be resolved beforehand. How does a city want to project itself in the domestic and foreign market? What type of investments will help it achieve this? What future does it hope to offer its residents?
The answers to these questions are valid for all cities, but particularly those with an economic, labor and social model closely associated to the now absent industrial sector.
Detroit is, in this case, a paradigmatic example. The North American city went from being a symbol of the automobile industry for practically the entire 20th century to a bankrupt city that had to react and begin practically from scratch.
Models that work

Post-industrial cities that have managed to change and prosper have implemented specific measures that make the most of that industrial legacy. Below are some examples.
Attracting cultural tourism
Changing the model does not necessarily involve the destruction of industrial symbols. On the contrary. In some cases, that industrial heritage can become a tool for promoting new economic activities, with a particular focus on tourism or they can become new venues for museums or cultural spaces.
Reconversion in contemporary architecture symbols
Another interesting alternative is choosing to grant new uses to the old industrial infrastructure, more closely adapted to current requirements and uses. An example is the High Line in New York, the work of Diller Scofidio + Renfro, which has transformed an abandoned transport line into a 2.5 kilometer elevated walkway with vegetation and featuring works of art.
Becoming a green city
In relation to the foregoing, other cities have chosen to transform old industrial spaces into green areas. Chicago’s 606 is a linear park built on an abandoned elevated rail line. Another example, also in the United States, is the Buffalo Bayou Park in Houston, which has revitalized kilometers of the industrialized and highly polluted riverbank for its residents.
Post-industrialized cities that have successfully transformed themselves
Numerous cities have completed their transformation into innovative and transformative models, opting for diverse strategies.
Turin
The capital of the region of Piamonte has started to strongly invest in creative and cultural strategies to change the old image of an industrial city, opting for two types of models: that of a smart city to attract national investments and a gastronomic haven aimed at the foreign market.
Pittsburgh
Strategy 21 is the name of the strategy designed by the city council, universities and the Commissioners of Allegheny County, which includes five projects to be conducted in 15 years. One of them is using its educational cluster to invest in technology research. The result was the creation of the CMU’s National Robotics Engineering Center, which has soon gone from being a regional center to the world’s most important robotics research and development institution.
Velenje
After the collapse of socialism and the independence from Slovenia in 1991, Velenje managed to transform itself and adapt to a market economy. Apart from focusing on mining, the city focused on the production of medium-technology machinery, electronics and electrical appliances, which together employ over 60% of the town’s total labor force.
Bilbao
This old Spanish industrial city related to steel and iron, began its transformation in 1992 with the creation of the Bilbao Ría 2000 agency to renovate degraded and industrial areas developing environmental, transport and urban development projects. These changes have allowed it to become an international city for the organization of conferences, musical and cultural events, with the Guggenheim Museum as the flagbearer of this reinvention.
Photographs | Unsplash/ Dominik Dancs, Unsplash/Elizabeth Villalta