Author | Lucía Burbano
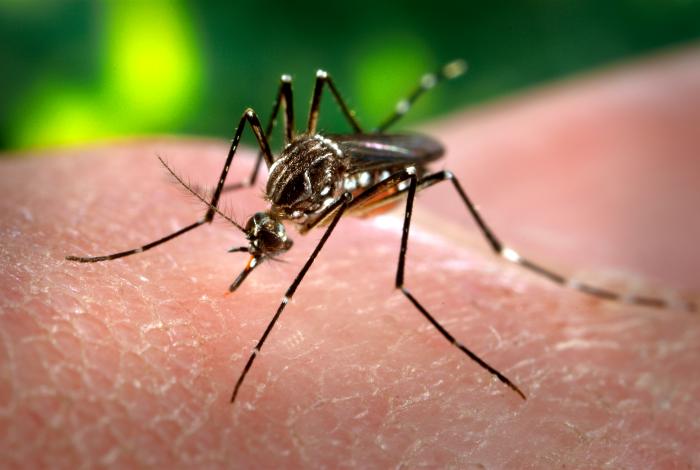
Apart from being irritating, mosquito bites can transmit diseases, some quite serious, such as the Zika virus or the West Nile virus, malaria or encephalitis. Controlling these insects is not easy and, according to the World Health Organization, 725,000 people die each year as a result of these insects. However, numerous cities are using strategies to prevent the spread of the insects and reduce the risk of transmission.
The mosquito, the most dangerous insect
Mosquitoes, which is Spanish and Portuguese for "little flies" and which are also called "zancudo" in some Latin American countries, are flying insects belonging to the Diptera family. In fact, there are over 3,500 types of mosquitoes that live in most regions of the world. They normally lay their eggs in stagnant waters and their larvae live in this medium, hence their presence being more intense in wetlands and other aquatic sources.
Adult mosquitoes live between 2 and 4 weeks, depending on the species and humidity and temperature conditions, among other environmental factors. The female mosquitoes tend to live longer than the males.
The female is the main cause of mosquito bites since they need to draw blood in order to produce eggs. The bites generally cause swelling or itching on the skin and sometimes they can transmit mild to severe infectious diseases.
Diseases that can be transmitted by mosquitoes
As they feed off blood, mosquitoes can get infected with diseases if they bite an infected person and then spread it to other people.
A few infected mosquitoes are capable of starting the following disease outbreaks:
Zika virus
This virus is caused by a virus transmitted primarily by Aedes mosquitoes, which bite during the day. Symptoms are generally mild and include fever, rash, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain, malaise or headache. Symptoms typically last for 2–7 days. Complications arise if it is transmitted during pregnancy, since it can cause congenital malformations, preterm birth and miscarriage.
Dengue
Common in tropical and subtropical areas of the world such as South East Asia, the Western Pacific Islands, Latin America and Africa. In its mildest version it causes high fever and flu-like symptoms. In its most serious version, dengue, also known as "hemorrhagic dengue fever", can cause intense bleeding, sudden drop in blood pressure and death.
Malaria
Malaria is caused by a bite by an infected Anopheles mosquito. Symptoms include fever, shivers, sweating and headache. In some cases it can cause jaundice, blood coagulation defects, shock, renal or hepatic failure and central nervous manifestations.
West Nile Virus
Generally, this virus presents mild symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, skin rashes or swollen lymph glands. However, if it enters the brain it can cause swelling called encephalitis or inflammation of the tissue that surrounds the brain and the spinal cord, called meningitis.
How can cities protect themselves from mosquitoes
Cities are used to combating ‘invisible’ enemies. Controlling mosquitoes can be divided into two areas of responsibility: the individual area and the public one. In terms of the public area, this is executed under the concept of Integrated Mosquito Management (IMM).
IMM is based on environmental, economic and social criteria and it integrates multidisciplinary pest management methodologies to protect public health, the environment and to improve quality of life.
The IMM strategies are numerous. These include the reduction or elimination of the insect in its own source through, among others, biological control, placing species of fish such as the western Mosquitofish, which feed on mosquito larvae, in marshes and ponds.

Other non-chemical control methods for adult mosquitoes are invertebrate predators. Adult mosquito biological control by means of birds, bats, dragonflies and frogs has been employed by various agencies.
Several smart cities have incorporated the fight against mosquitoes in their strategies, with Singapore being a case study.
Places that have already achieved it
The rural town of Ifakara, also known as ‘Mosquito City’, in Tanzania, hosts the world’s largest captive mosquito colony. It is, quite literally, a laboratory where they study methods to combat malaria and other diseases transmitted by these insects, how to catch them, repel them and eliminate them. For example, they have discovered that mosquitoes use their memory to return to a household where they last obtained blood.
A pilot study was also launched in Colombia in 2018 using a mobile app created by Premise, a U.S. data and analysis company to identify and subsequently destroy mosquito breeding grounds.
All the collected data were recorded, georeferenced, photographed and finally submitted to the health authorities so they could take the corresponding action and to educate the community on how to eradicate colonies of mosquitoes.
Given the scope of the public health threat due to mosquito-borne diseases, it is vital for cities with climates that favor the spread of mosquitoes to implement measures to avoid this. Appropriate public drainageis essential in order to prevent the appearance of larvae, and it is also vital to monitor municipal water deposits.
Photographs | Wikipedia Commons, Wikipedia Commons