Author | M. Martínez Euklidiadas
If during the 20th century the aim in cities was to make space for private vehicles, one of the challenges of the 21st century is to correct that self-destructive trend. The proximity city, also known as walkable city emerged as a basic town-planning tool aimed at improving the quality of life of residents and reducing their impact.
What is a walkable city?
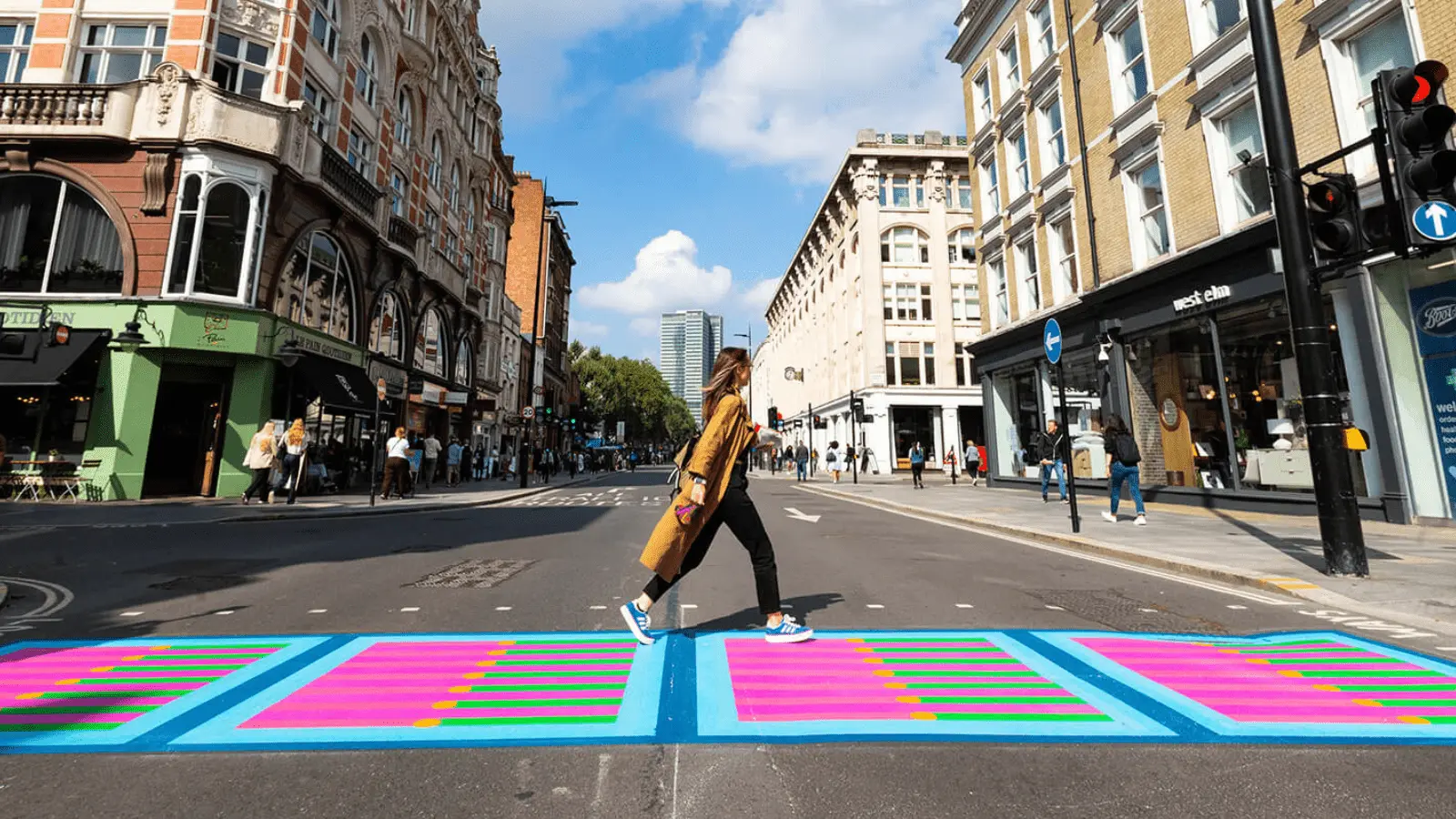
A walkable city, also known as a 15-minute city, refers to a compact form of urbanism in which citizens are able to access basic and essential services within a reasonable distance.
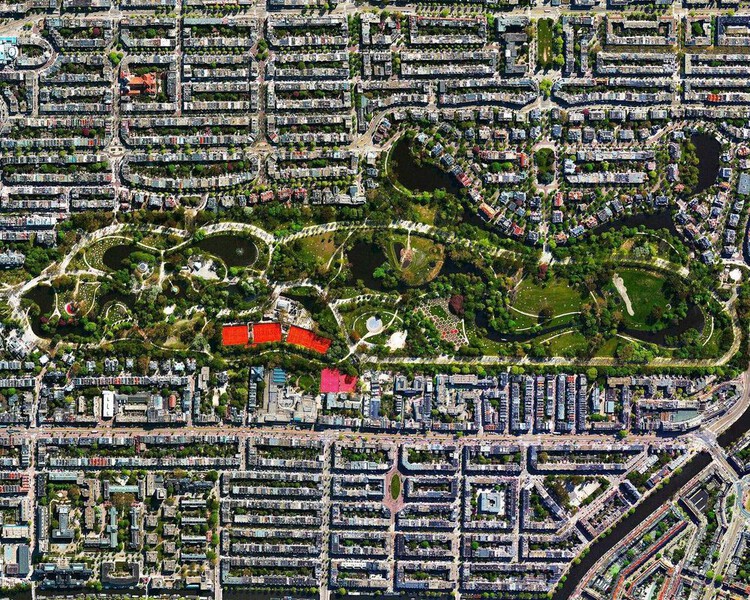
The concept of walkable indicates that it is possible to meet the requirements of a sustainable, fairer, healthier and quality life, within a reasonable distance. An isochrone can be drawn on the map of a city, an area that is ‘reachable’ within a 15-minute walk or bike trip. The image below shows six isochrones in Barcelona for pedestrians.

Characteristics of a walkable city
A walkable city has the following characteristics:
- Decentralization. The idea is that within these ’15-minute areas’, there are stores, sports facilities, schools and institutes (but not universities), health centers (not hospitals), neighborhood libraries, ample parks, etc., so they are distributed across the city and not concentrated.
- Urban density. It is essential to have a minimum density called ‘critical mass’, which, apart from bringing services nearer and making them more affordable, significantly reduces the impact per capita of residents by sharing more infrastructures. It is the opposite of the harmful urban sprawl, although, without the need for skyscrapers.
- Neighborhood The walkable concept is related to neighborhoods or communities, urban and street life, the associative fabric, as opposed to the commuter town in which social relations barely exist. The aim is to create places, spaces in which to live.
- Low speed. In these ‘urban hubs’, as the UN describes these neighborhoods given their degree of urbanization, there are speeds that are compatible with human features and a mobility made up, predominantly, of pedestrians or cyclists. Apart from sustainable, this form of mobility does not produce gas emissions or noise.
- Care. As a result of the foregoing, in this form of urbanism, space is given to the area of care, which is normally ignored and often rejected in favor of "productive" services. This is an inclusive social phenomenon that includes vulnerable groups.
The challenges of the 15-minute city

The walkable city first emerged in around 1900 as a Utopian concept, but it later emerged during the 21st century as a necessity to ensure environmental protection, quality of life, energy security and as a means of closing social fractures, among other factors. Even so, it is not without its challenges.
- Gentrification. In these neighborhoods, quality of life increases and demand for this does too. Without putting a limit on the price per square meter, gentrification may emerge and create a split between the rich and poor.
- Border effect. The hypothetical border effect would appear when the previously internal traffic increases its intensity on the outskirts. At the moment this has not happened, but it could if these areas are not planned correctly.
- Social barriers. One of the most significant challenges of pedestrianizing cities, establishing bike lanes, building super-blocks, etc., is the social barrier to the privilege of private vehicles. 15-minute cities cannot be built without removing many cars from the roads.
Images | Maksim Zhashkevych, Openroute Service, Nick Night